Why is the Old Testament important to us?
Timothy emphasizes that “All Scripture is God-breathed.” The amazing unity of theme and purpose make it nothing less than the living word of God.
Hear Audio
In this journey...
We understand:
- The infallibility of the Scriptures
- Their consistency through historical ages
- The authenticity and timelessness of the sources
Introduction
The Bible is :
- Divinely inspired
- Divinely compiled
- And has transforming power
2 Timothy 3:16 All Scripture is God-breathed and is useful for teaching, rebuking, correcting and training in righteousness.
Christ’s Last Command
Christ wanted His disciples to learn and teach everything he taught them. Not just a part.
Matt 28:19 Therefore go and make disciples of all nations, baptizing them in the name of the Father and of the Son and of the Holy Spirit, 20 and teaching them to obey everything I have commanded you. And surely I am with you always, to the very end of the age.”
Great Diversity
The Bible is written by 40 authors:
- In two major languages (and a minor)
- With various occupations
- In 3 continents
- In 66 books (39 Old Testament books + 27 in the New Testament)
- Over a period of 1600 years
Yet converging in the following ways.
Amazing Unity
The Bible has:
One theme : There is one true God
One purpose : Redemption of mankind
One Saviour : Jesus Christ
Old Testament (OT) Book Summary(39 books)
Law
- Genesis to Deuteronomy
History
- Joshua to Esther
Poetry
- Job to Song of Solomon
Major Prophets
- Isaiah to Daniel
Minor Prophets
- Hosea to Malachi
New Testament (NT) Book Summary(27 books)
Gospels
- Matthew to John
History
- Acts
Paul’s Letters
- Romans to Philemon
Powerful Letters
- Hebrews to Jude
Prophecy
- Revelation
Old Testament Sources
There are seven known sources from which our modern Bibles have been directly or indirectly derived:
1. Masoretic Text
2. Dead Sea Scrolls
3. The Septuagint
4. Nash Papyrus
5. Cairo Geniza Fragments
6. Syriac Peshitta
7. Latin Vulgate
1. Masoretic Text
- Most Bibles are based on the Masoretic text.
- Dated from 7th to 11th centuries AD.
- “Masorites of Tiberias” created a school on the shores of the Sea of Galilee.
2. Dead Sea Scrolls
- Discovered between 1947 and 1954 in caves near Qumran, 20 km East of Jerusalem,
- Oldest known Hebrew OT text, written between 150 BC and 70 AD.
- There were more than 15,000 fragments and 500 manuscripts, contained in 900 separate scrolls.
- They contain every book of the Old Testament except Esther
3. The Septuagint (LXX)
This is:
- The Greek translation of OT
- Translated between the 3rd and 2nd BC
- Quoted in NT and by early Church Fathers.
- The basis for old Latin, Slavonic, Syriac, old Armenian, old Georgian and Coptic translations.
4. Nash Papyrus
- Dates approximately 150-100 BC
- Was housed at Cambridge University.
- Contains text of the Ten Commandments,
5. Cairo Geniza Fragments
- Geniza is a storeroom to keep writings on God, to treat them with respect, before burying them.
- We now have almost 300,000 fragments dating from 870 through to the late 1800′s.
6. Syriac Peshitta
- Translated during the second century directly from the Hebrew into Syriac, a dialect of Aramaic.
- Peshitta means “simple” or “direct” translation.
- Housed in the British Library, London, Milan, Paris, etc. dating from 6th, 7th, 8th centuries.
7. Latin Vulgate
- Latin translation of the Bible by Jerome.
- It was independent of the Hebrew, with the exception of Psalms.
- Completed in 405 AD.
- Dates from the start of the 8th century.
Establishing the Foundations
The Council of Nicea – represented by all Christendom and led by Emperor Constantine- put together the “Nicene Creed”, and foundations of the faith in 325 AD.
Compiling the Canon
In 367 AD, Athanasius provided listing of the 66 books. Inputs/ endorsements were also from:
- Ignatius of Antioch (A.D. 115).
- Polycarp, a disciple of John (A.D.108)
- Irenaeus (A.D. 185).
- Hippolytus (A.D. 170-235). [1][2]
- the Council of Laodicea (AD 363)
- The Council of Hippo (AD 393)
- Council of Carthage (AD 397).
There was much less controversy over OT books, with exception of Apocrypha (Catholic inclusions in 1546 AD)
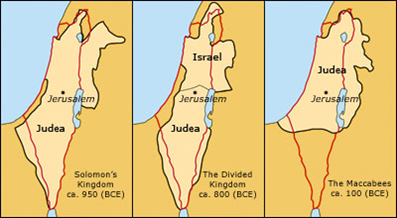
Israel under Foreign Rule
- In 931 BC the kingdom was divided into a southern part -Judea, and Israel in the north.
- 722 (BC) – Governed by the Assyrians
- 586 (BC) – Governed by the Babylonians
- 538 (BC) – Governed by the Persians
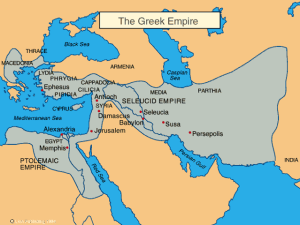
- 332 (BC) – Governed by the Greeks
- 164 (BC) – Governed by the Maccabees (One sect of Jews)
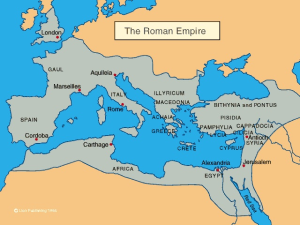
- 63 (BC) – The Roman Conquest
The Re-gathering of Israel – Last Three Centuries
While Jews were scattered, persecuted, tortured and killed in large numbers following Christ’s death:
- The waste desert land of Israel started becoming irrigated by returning Jews as prophesied
- The nation which did not exist was reborn (1948)
- Israel is the only Jehovah-worshipping nation in the world
Is it coming together for Christ’s second coming?
Discussion
- What has been your biggest obstacle in reading the OT ?
- Is OT only a book of history written by different people at different times? If not, what are the other benefits of OT ?
- How can you relate OT to the New Testament (NT)?
- How can you relate OT to the present times ?
References
- Canon of Scripture by FF Bruce,
- Logos Bible software
- biblica.com